Intro
Along with several other new features, VCF Operations Orchestrator 9.x comes with an updated Rhino Engine which is the backend execution engine to execute all the JavaScript code that we run inside Orchestrator. This newer Rhino Engine (version 1.7.15) comes with various new ECMAScript features as new as ES2022.
However, there is a catch. Orchestrator is inherently built in a way that not all Rhino Engine supported features are implemented inside it. For eg, Rhino Engine 1.7.15 supports classes but Orchestrator 9.x doesn’t.
So, to tackle this and to figure out which feature is supported and which is not, I spend a lot of time to carefully analyze the execution behaviors of Orchestrator. Check out the following table to get the complete feature sets available in Orchestrator:
- “ ” signifies that the Orchestrator has an opposite support stance to a feature than that of Rhino Engine. For e.g. Rhino Engine 1.7.15 support classes, spread operator, etc. but Orchestrator 9.x doesn’t.
- “ ” indicates that the feature support is consistent in both the Rhino Engine and the Orchestrator.
| VCF Orchestrator Features | Orchestrator 8.x | Orchestrator 9.x |
|---|---|---|
| ECMAScript Version | ES5 (ECMAScript 5.1) | ES5 + ES2015-ES2022 features |
| JavaScript Version (Default) | JavaScript 1.7 | JavaScript 1.7+ |
| Rhino Engine version | 1.7R4 | 1.7.15 |
| Arrow Functions | No | Yes |
| Classes | No | Yes |
| Template Literals | No | Yes |
| Destructuring Assignment | Partial (JS 1.7) | Yes |
| Default Parameters | No | Yes |
| Rest Parameters | No | Yes (basic) |
| Spread Operator | No | Yes |
| Let and Const | Basic (limited) | Full support |
| For…of loops | No | Yes |
| Promises | No | Yes |
| Generators (function*) | Yes (JS 1.7 style) | Yes (ES6 style) |
| Symbols | No | Yes |
| Map/Set | No | Yes |
| Proxies | No | Yes |
| Reflect API | No | Yes |
| Symbol.species | No | Yes |
| Super keyword | No | Yes |
| Exponentiation Operator (**) | No | Yes |
| Array.prototype.includes | No | Yes |
| Async/Await | No | No |
| Object.values/entries | No | Yes |
| Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors | No | Yes |
| String padding | No | Yes |
| Rest/Spread Properties | No | Partial |
| Async Iteration | No | No |
| Promise.finally | No | Yes |
| Array.flat/flatMap | No | Yes |
| Object.fromEntries | No | Yes |
| Optional Catch Binding | No | Yes |
| String.trimStart/trimEnd | No | Yes |
| Optional Chaining (?.) | No | No |
| Nullish Coalescing (??) | No | No |
| BigInt | No | Yes |
| Promise.allSettled | No | Yes |
| globalThis | No | Yes |
| Logical Assignment (||=, &&=) | No | No |
| Numeric Separators | No | No |
| String.replaceAll | No | No |
| Object.hasOwn | No | Yes |
| Array.at() | No | No |
| Top-level await | No | No |
| Iterators | Yes | Yes |
| Array Comprehensions | Yes | Yes |
| Block Scope with let | Yes | Yes |
| Expression Closures | Partial | Yes |
| Regex Sticky Flag (y) | No | Yes |
| Regex Unicode Flag (u) | No | Partial |
| JSON Superset | No | Yes |
| String.raw | No | Yes |
| Number.EPSILON | No | Yes |
| E4X (XML) | Yes | Yes |
| Strict Mode | Partial | Full |
| Java Interoperability | Yes | Enhanced |
| Console API (console.log) | No | Yes (built-in) |
| Error.stack property | No | Yes |
| INTL (Internationalization) | No | Basic (INTL_402 flag) |
Just a heads up: This post isn’t set in stone, since there might be times when we find out a feature is only partially supported, or that some non-supported features have cool functionalities we can actually use. I may not get to test everything right away, but I’ll definitely give it a shot as time goes on. I really appreciate it when my readers chime in with any thoughts or observations, so feel free to let me know what you notice!
Arrow Functions ✅
// Basic arrow function
var add = (a, b) => a + b;
System.log(add(5, 3)); // 8
// With array methods
var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
var doubled = numbers.map(n => n * 2);
System.log(doubled); // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
// Filter with arrow function
var evens = numbers.filter(n => n % 2 === 0);
System.log(evens); // [2, 4]
// Arrow function with block
var greet = name => {
var message = "Hello, " + name;
return message;
};
System.log(greet("World")); // Hello, World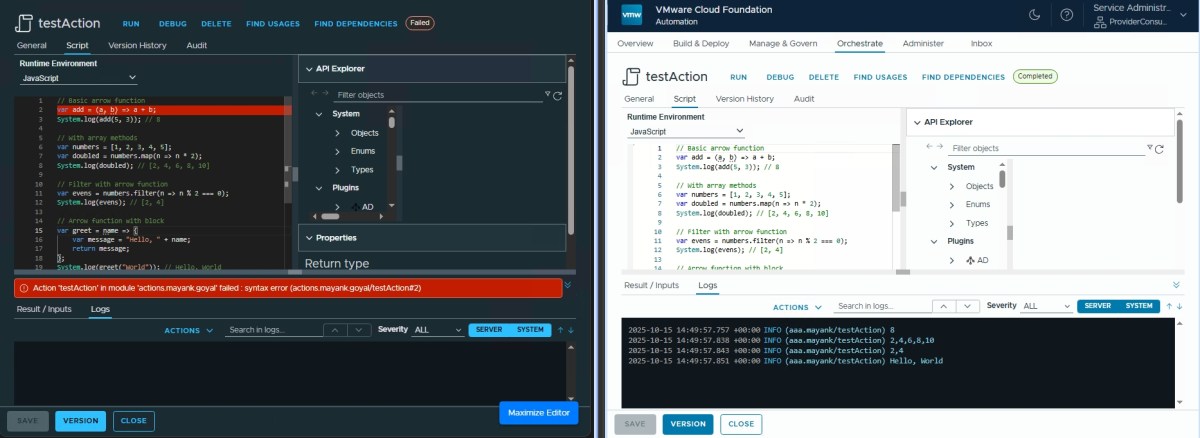
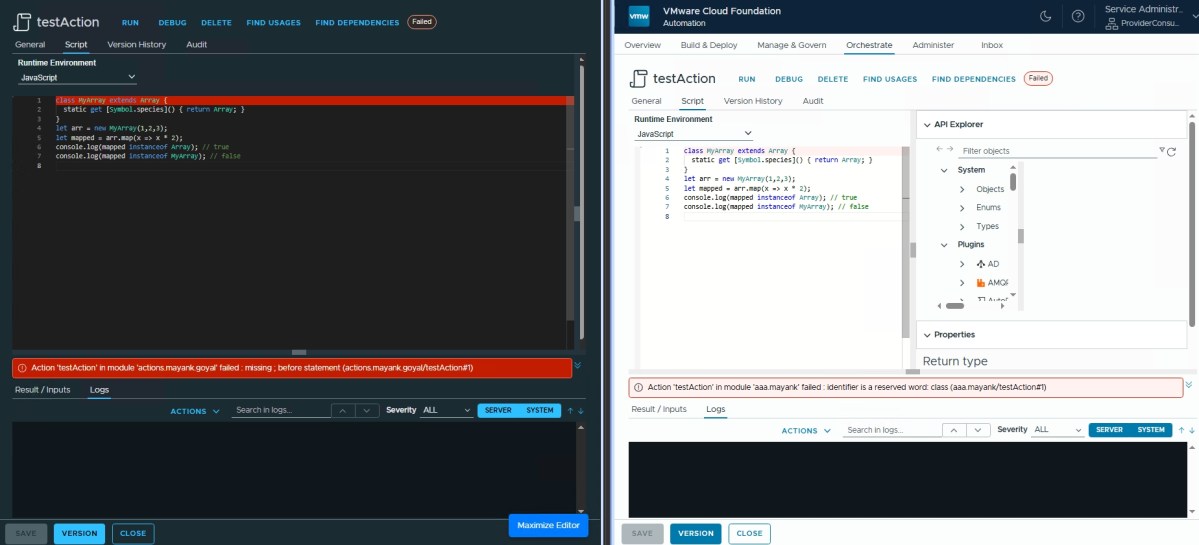
Classes ❌
You still can’t use class keyword in Orchestrator 9.x as it throws error saying “class identifier is a reserved word”.
Template Literals ✅
// Template literals with interpolation
var name = "World";
var greeting = `Hello, ${name}!`;
System.log(greeting); // Hello, World!
// Multi-line strings
var multiLine = `This is line 1
This is line 2
This is line 3`;
System.log(multiLine);
// Expression evaluation
var a = 10, b = 20;
var result = `The sum of ${a} and ${b} is ${a + b}`;
System.log(result); // The sum of 10 and 20 is 30
// String.raw for raw strings
var path = String.raw`C:\Users\Admin\Documents`;
System.log(path); // C:\Users\Admin\Documents

BigInt ✅
// BigInt for large integers
var bigNum = 9007199254740991n;
var anotherBig = BigInt("9007199254740992");
System.log(bigNum + 1n); // 9007199254740992n
System.log(anotherBig * 2n); // 18014398509481984n
// Math with BigInt
var result = 100n ** 50n;
System.log(result); // Very large number
// Cannot mix BigInt and Number
// var bad = 10n + 5; // TypeError
var good = 10n + BigInt(5);
System.log(good); // 15n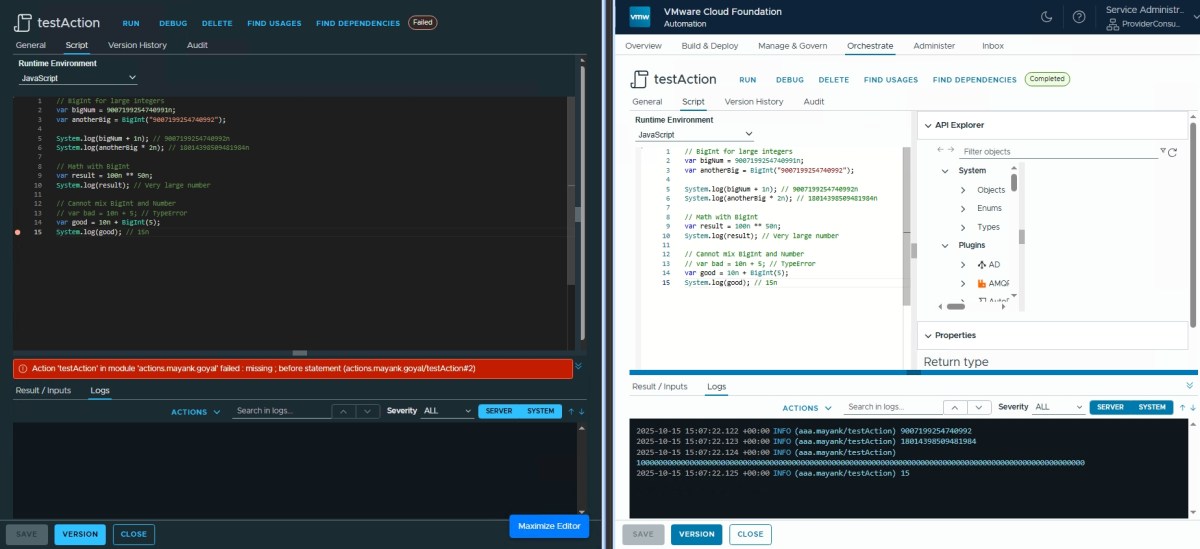
Destructuring Assignment ❌
// Object destructuring
var person = { name: "John", age: 30, city: "NYC" };
var { name, age } = person;
System.log(name); // John
System.log(age); // 30
// With default values
var { country = "USA" } = person;
System.log(country); // USA
// Renaming
var { name: fullName } = person;
System.log(fullName); // John
// Nested destructuring
var user = {
id: 1,
details: {
name: "Alice",
email: "alice@example.com"
}
};
var { details: { name: userName, email } } = user;
System.log(userName); // Alice
System.log(email); // alice@example.com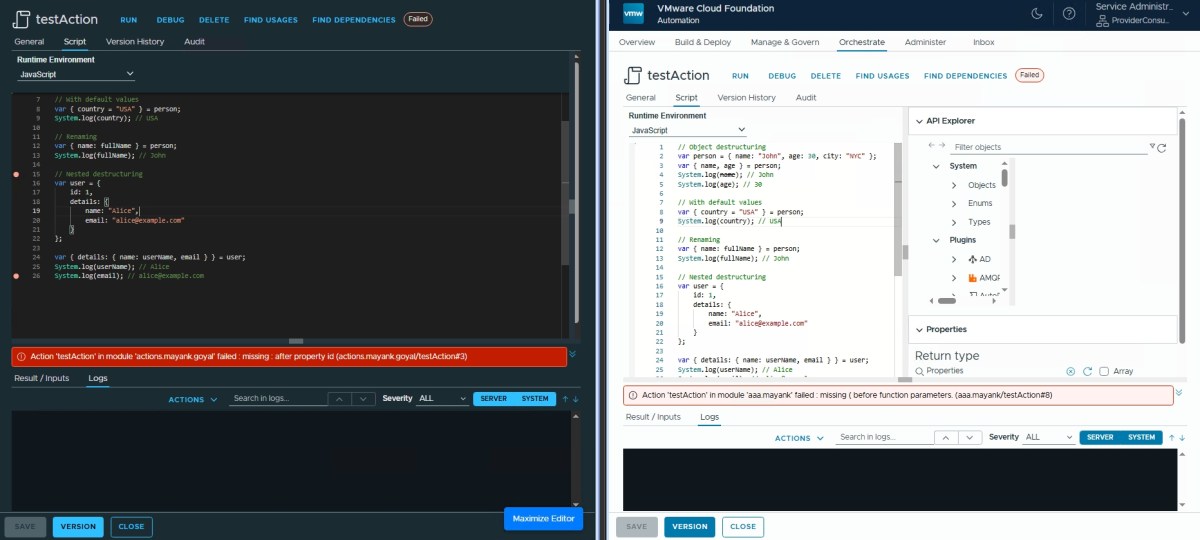
Default Parameters ❌
Not supported in both the Orchestrator versions.
// Default parameter values
function greet(name = "Guest", greeting = "Hello") {
return greeting + ", " + name + "!";
}
System.log(greet()); // Hello, Guest!
System.log(greet("Alice")); // Hello, Alice!
System.log(greet("Bob", "Hi")); // Hi, Bob!
// Default with expressions
function createArray(length = 10, fill = 0) {
return Array(length).fill(fill);
}
System.log(createArray(5, 1)); // [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
System.log(createArray(3)); // [0, 0, 0]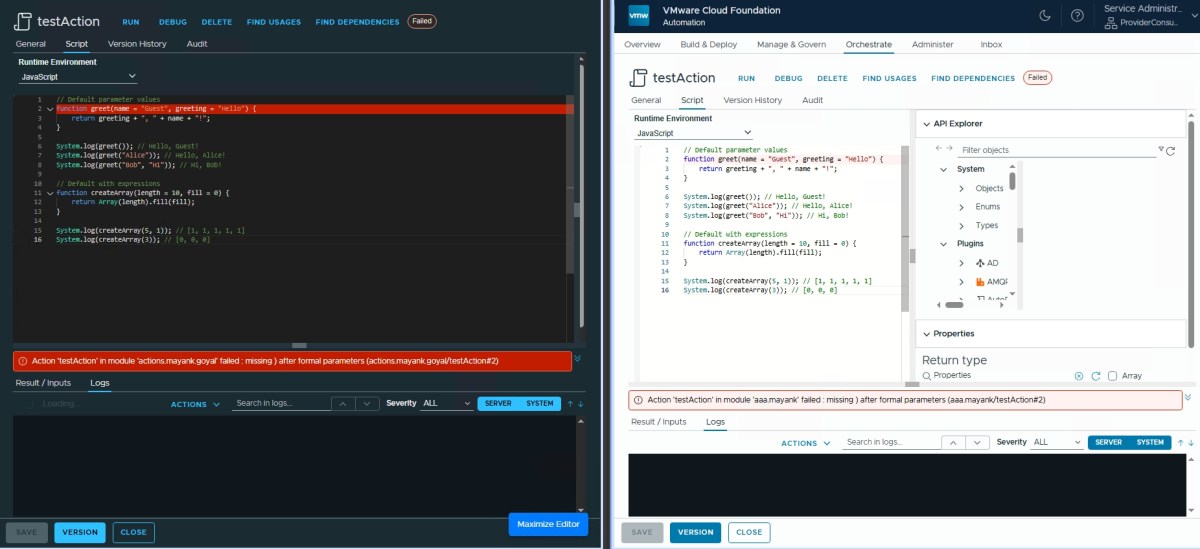
Rest Parameters ✅
// Rest parameters
function sum(...numbers) {
return numbers.reduce((acc, num) => acc + num, 0);
}
System.log(sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); // 15
System.log(sum(10, 20)); // 30
// Rest with other parameters
function greetAll(greeting, ...names) {
return names.map(name => greeting + ", " + name).join(" | ");
}
System.log(greetAll("Hello", "Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"));
// Hello, Alice | Hello, Bob | Hello, Charlie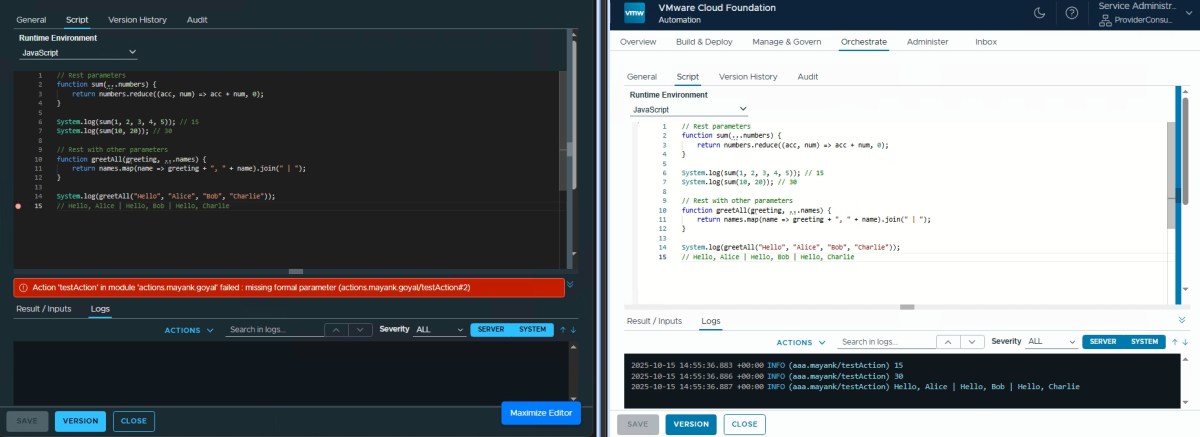
Spread Operator ❌
// Spread in arrays
var arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
var arr2 = [4, 5, 6];
var combined = [...arr1, ...arr2];
System.log(combined); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
// Spread in function calls
var numbers = [5, 10, 15];
System.log(Math.max(...numbers)); // 15
// Copy array
var original = [1, 2, 3];
var copy = [...original];
copy.push(4);
System.log(original); // [1, 2, 3]
System.log(copy); // [1, 2, 3, 4]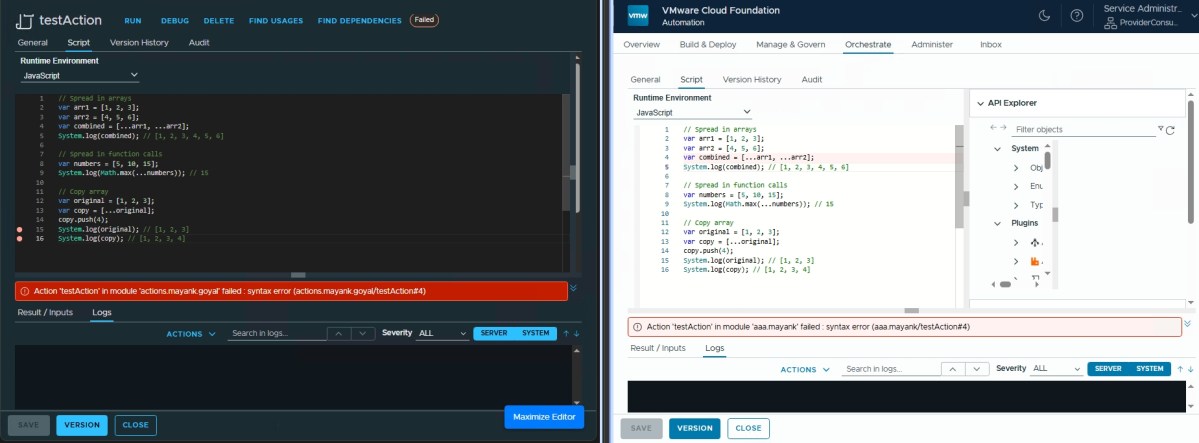
Let and Const ✅
Finally, let is there now.
// const - cannot be reassigned
const PI = 3.14159;
System.log(PI); // 3.14159
// PI = 3.14; // Error: Assignment to constant variable
// let - block scoped
function testScope() {
let x = 10;
if (true) {
let x = 20;
System.log(x); // 20
}
System.log(x); // 10
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.log(i); // 0, 1, 2
}
// System.log(i); // Error: i is not defined
}
testScope();
// Const with objects (properties can be modified)
const config = { debug: true };
config.debug = false; // OK
config.timeout = 5000; // OK
System.log(config); // { debug: false, timeout: 5000 }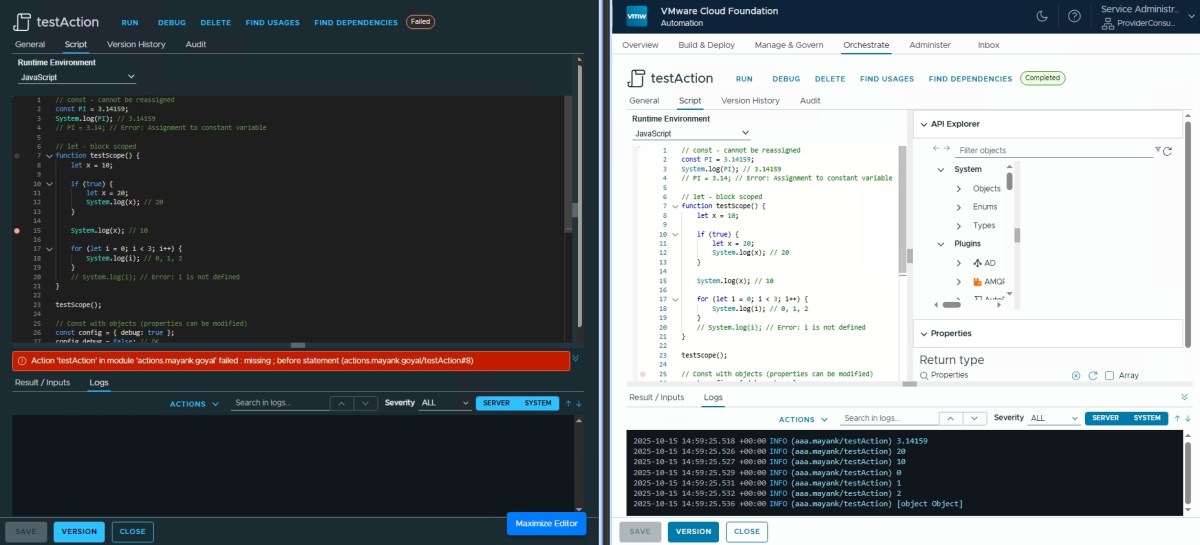
For…of Loops & Map/Set✅
// Iterate over array
var fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"];
for (var fruit of fruits) {
System.log(fruit);
}
// Iterate over string
for (var char of "Hello") {
System.log(char); // H, e, l, l, o
}
// Iterate over Map
var map = new Map();
map.set("a", 1);
map.set("b", 2);
for (var [key, value] of map) {
System.log(key + " = " + value);
}
// Iterate over Set
var set = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
for (var num of set) {
System.log(num);
}
Promises ✅
// Creating a promise
function asyncOperation(value) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
if (value > 0) {
resolve("Success: " + value);
} else {
reject("Error: Invalid value");
}
});
}
// Using promises
asyncOperation(10)
.then(function(result) {
System.log(result); // Success: 10
return asyncOperation(20);
})
.then(function(result) {
System.log(result); // Success: 20
})
.catch(function(error) {
System.log(error);
});
// Promise.all
var promises = [
asyncOperation(1),
asyncOperation(2),
asyncOperation(3)
];
Promise.all(promises).then(function(results) {
System.log(results); // ["Success: 1", "Success: 2", "Success: 3"]
});
Generators (function*) ✅
// Generator function (JS 1.7 style)
function* fibonacci() {
var a = 0, b = 1;
while (true) {
yield a;
var temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp + b;
}
}
var fib = fibonacci();
System.log(fib.next()); // 0
System.log(fib.next()); // 1
System.log(fib.next()); // 1
System.log(fib.next()); // 2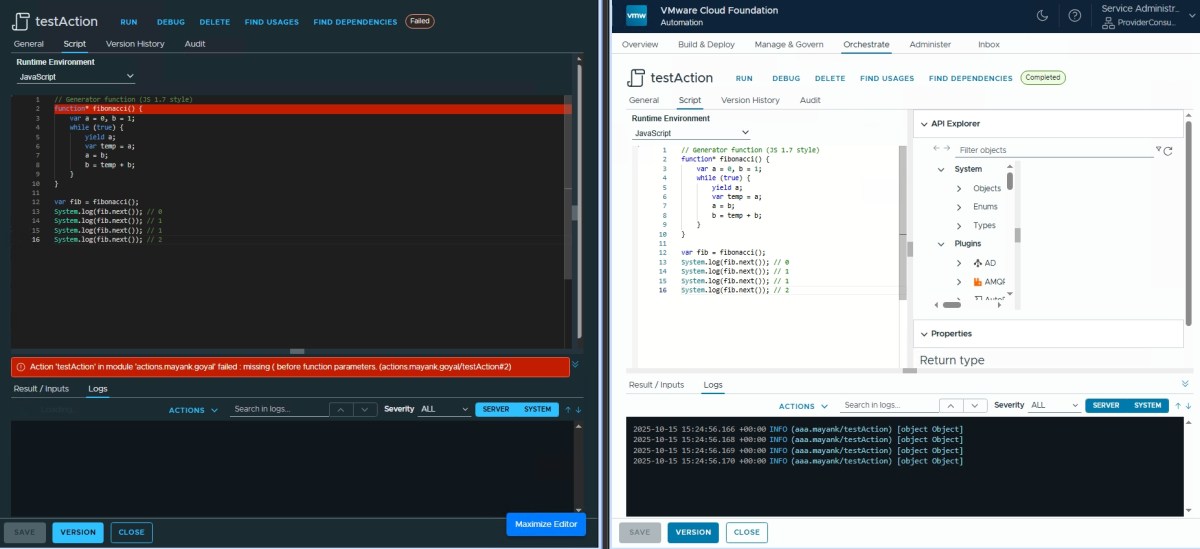
Symbols ✅
// Create symbols
var sym1 = Symbol("description");
var sym2 = Symbol("description");
System.log(sym1 === sym2); // false - each symbol is unique
// Symbol as object property
var obj = {};
var privateKey = Symbol("private");
obj[privateKey] = "secret value";
System.log(obj[privateKey]); // secret value
System.log(Object.keys(obj)); // [] - symbols not enumerable
// Well-known symbols
var myArray = [1, 2, 3];
var iterator = myArray[Symbol.iterator]();
System.log(iterator.next()); // { value: 1, done: false }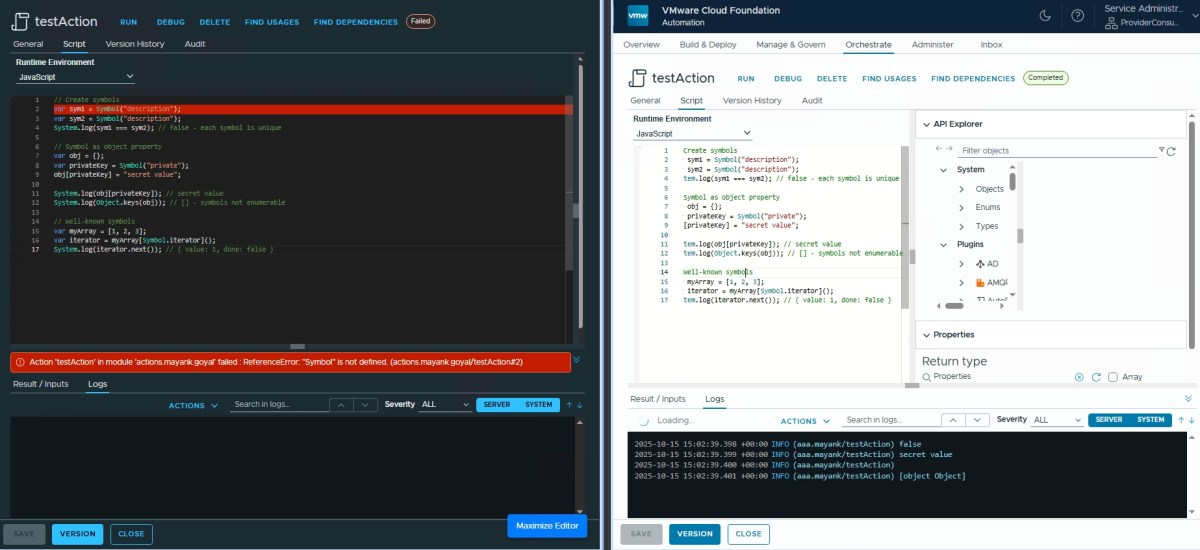
Proxies ❌
// Proxy for object interception
var target = { name: "Alice", age: 30 };
var handler = {
get: function(obj, prop) {
console.log("Getting property: " + prop);
return prop in obj ? obj[prop] : "Property not found";
},
set: function(obj, prop, value) {
console.log("Setting " + prop + " = " + value);
obj[prop] = value;
return true;
}
};
var proxy = new Proxy(target, handler);
System.log(proxy.name); // Logs: Getting property: name, then: Alice
proxy.age = 31; // Logs: Setting age = 31
// Reflect API
System.log(Reflect.has(target, "name")); // true
System.log(Reflect.get(target, "age")); // 31
Reflect.set(target, "city", "NYC");
System.log(Reflect.ownKeys(target)); // ["name", "age", "city"]
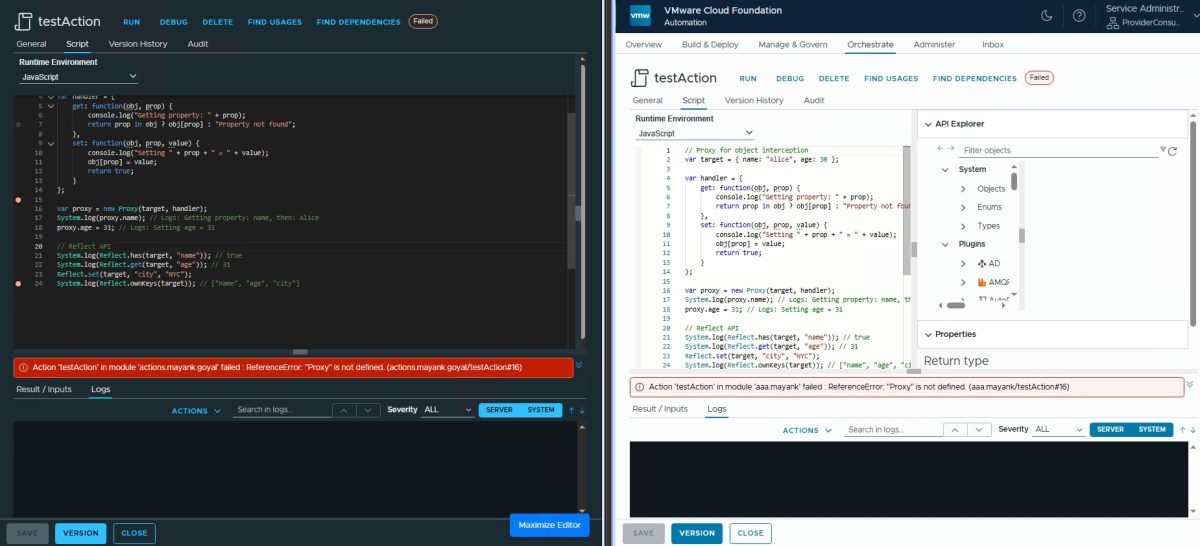
Reflect API ❔
let obj = {}; Reflect.set(obj, "x", 42);
System.log(obj.x);TO BE TESTED…
Symbol.species ❌
class MyArr extends Array {
static get [Symbol.species]() { return Array; }
}
let arr = new MyArr(1,2,3);
let mapped = arr.map(x => x*2);
System.log(mapped instanceof Array);
System.log(mapped instanceof MyArr); You cannot set or use [Symbol.species] on a plain object or array directly without using a class and class is not supported in Orchestrator.
Super Keyword ❌
class Parent { say() { return "Hello"; } }
class Kid extends Parent { say() { return super.say() + " World"; } }
System.log(new Kid().say());You cannot use super without using a class and class is not supported in Orchestrator.
Exponentiation Operator (**) ✅
// Exponentiation operator
System.log(2 ** 3); // 8
System.log(5 ** 2); // 25
System.log(10 ** -1); // 0.1
// Equivalent to Math.pow
System.log(2 ** 3 === Math.pow(2, 3)); // true
// Assignment
var num = 2;
num **= 3;
System.log(num); // 8
Array includes() ✅
System.log([1,2,3].includes(2));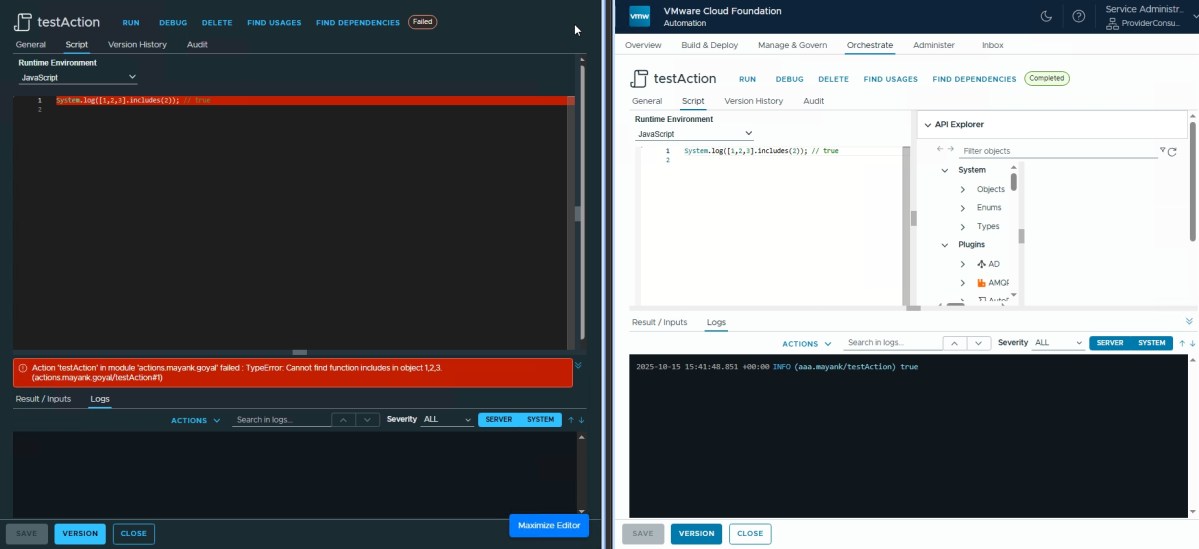
Async/Await ❌
Still not supported in Rhino 1.7.15 (Orchestrator 9.x).
Object.values/entries ✅
// Object.values
var person = { name: "Alice", age: 30, city: "NYC" };
var values = Object.values(person);
System.log(values); // ["Alice", 30, "NYC"]
// Object.entries
var entries = Object.entries(person);
System.log(entries); // [["name", "Alice"], ["age", 30], ["city", "NYC"]]
// Iterate over entries
for (var [key, value] of Object.entries(person)) {
System.log(key + ": " + value);
}
// Output:
// name: Alice
// age: 30
// city: NYC
// Object.fromEntries (ES2019)
var arr = [["a", 1], ["b", 2], ["c", 3]];
var obj = Object.fromEntries(arr);
System.log(obj); // { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 }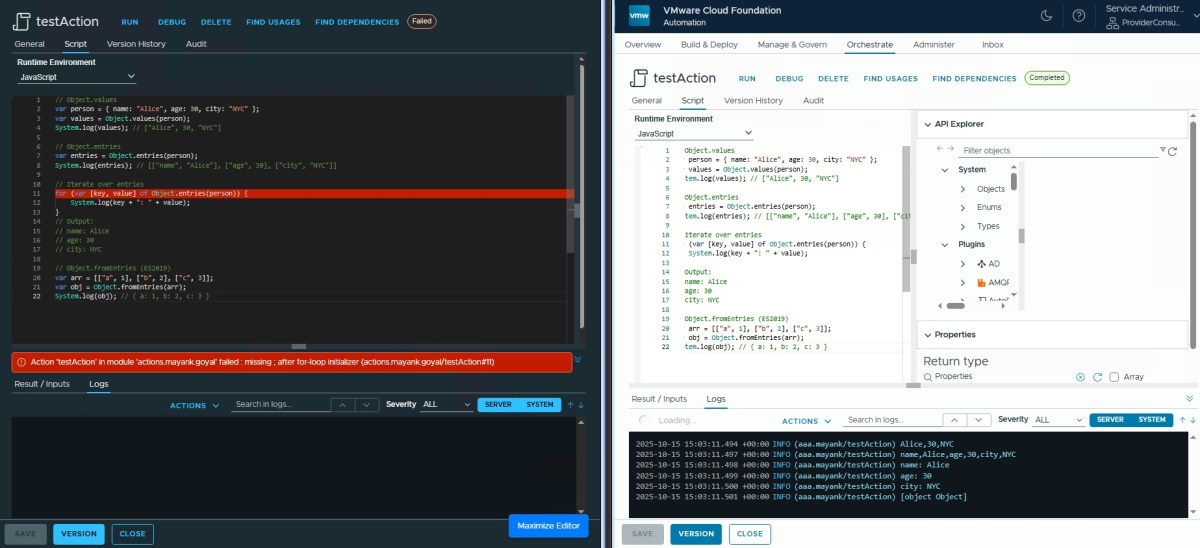
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors ✅
// Get all property descriptors
var obj = {
name: "Test",
value: 42
};
var descriptors = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj);
System.log(descriptors);
/* Output:
{
name: {
value: "Test",
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true
},
value: {
value: 42,
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true
}
}
*/
// Useful for cloning objects with getters/setters
var source = {
get foo() { return "bar"; }
};
var clone = Object.create(
Object.getPrototypeOf(source),
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(source)
);
System.log(clone.foo); // "bar"
String Padding ✅
System.log("42".padStart(5, "0")); // "00042"
System.log("42".padEnd(5, "-")); // "42---"
Async Iteration ❌
Still not supported in Rhino 1.7.15 (Orchestrator 9.x).
Promise.finally ✅
Promise.resolve(123).finally(() => System.log("Done"));
Array.flat/flatMap ✅
// Array.flat - flatten nested arrays
var nested = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]];
System.log(nested.flat()); // [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]]
System.log(nested.flat(2)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
// flatMap - map and flatten
var numbers = [1, 2, 3];
var result = numbers.flatMap(x => [x, x * 2]);
System.log(result); // [1, 2, 2, 4, 3, 6]
// Useful for transformations
var sentences = ["Hello World", "Foo Bar"];
var words = sentences.flatMap(s => s.split(" "));
System.log(words); // ["Hello", "World", "Foo", "Bar"]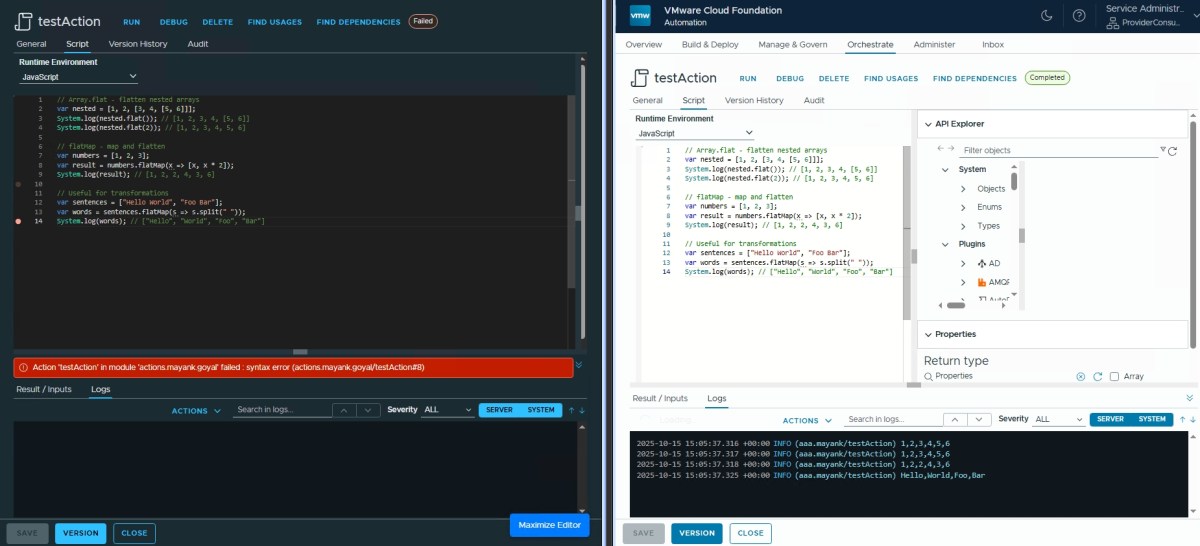
Object.fromEntries ✅
System.log(Object.fromEntries([["a",1],["b",2]])); // {a:1, b:2}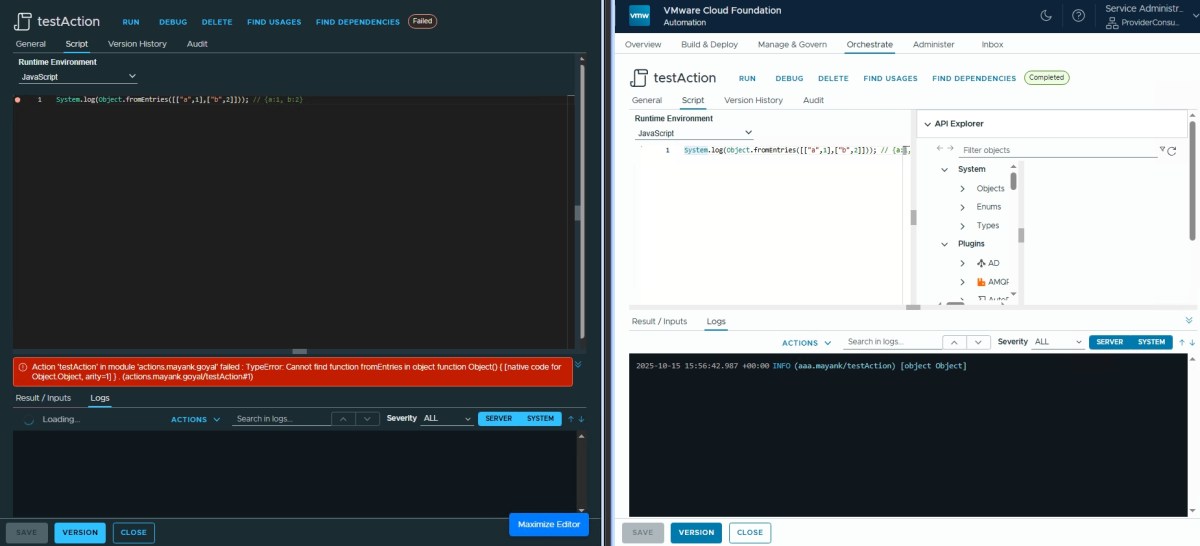
Optional Catch Binding (catch without parameter) ✅
// Catch without parameter
try {
throw new Error("Something went wrong");
} catch {
// No need to bind the error if not used
System.log("An error occurred");
}
// Traditional way (still works)
try {
throw new Error("Another error");
} catch (e) {
System.log("Error: " + e.message);
}
Numeric Separators ✅
let big = 1_000_000;
console.log(big); // 1000000
Array.at() ✅
System.log([10,20,30].at(-1)); // 30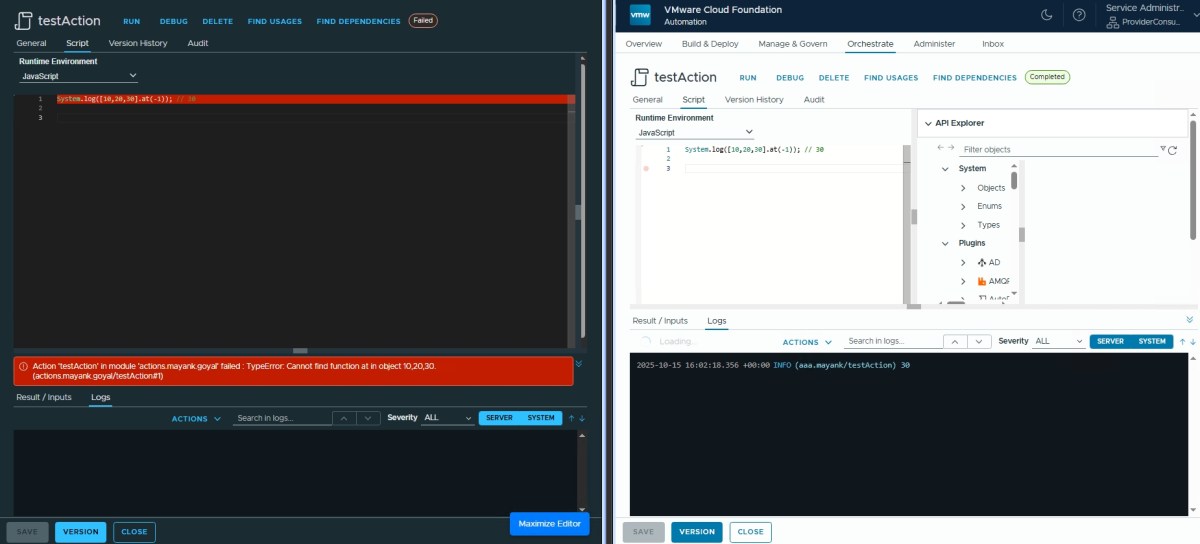
String.replaceAll ✅
console.log("a,b,c".replaceAll(",", "|")); // "a|b|c"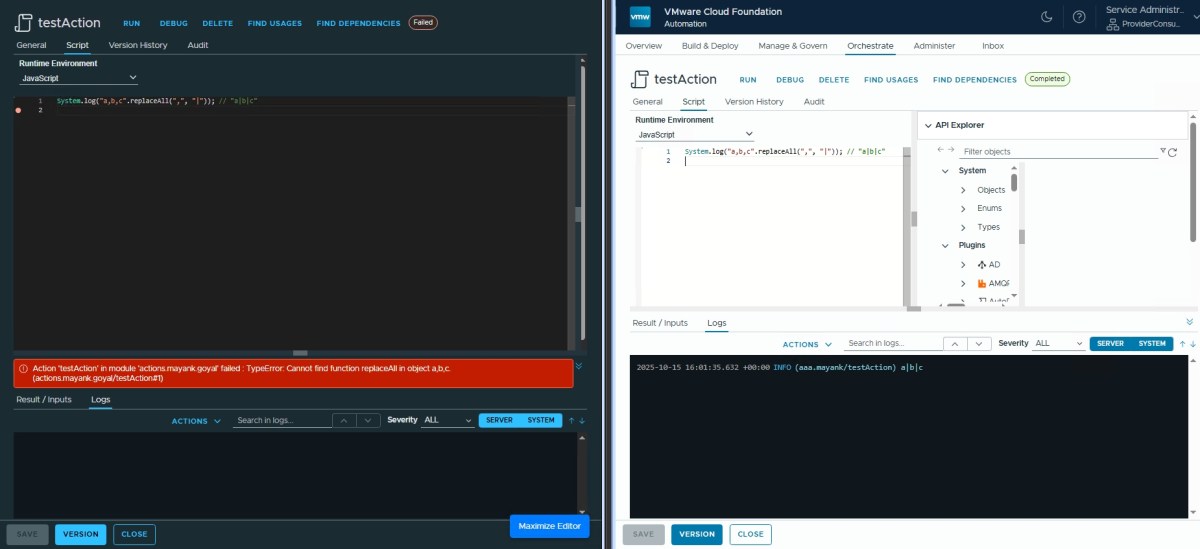
Nullish Coalescing (??) ❌
let val = null;
System.log(val ?? "default"); // "default"TO BE TESTED…
Optional Chaining ❌
const obj = {
greet() { return "Hello!"; }
};
console.log(obj.greet?.()); // "Hello!"
console.log(obj.sayBye?.()); // undefined (no error)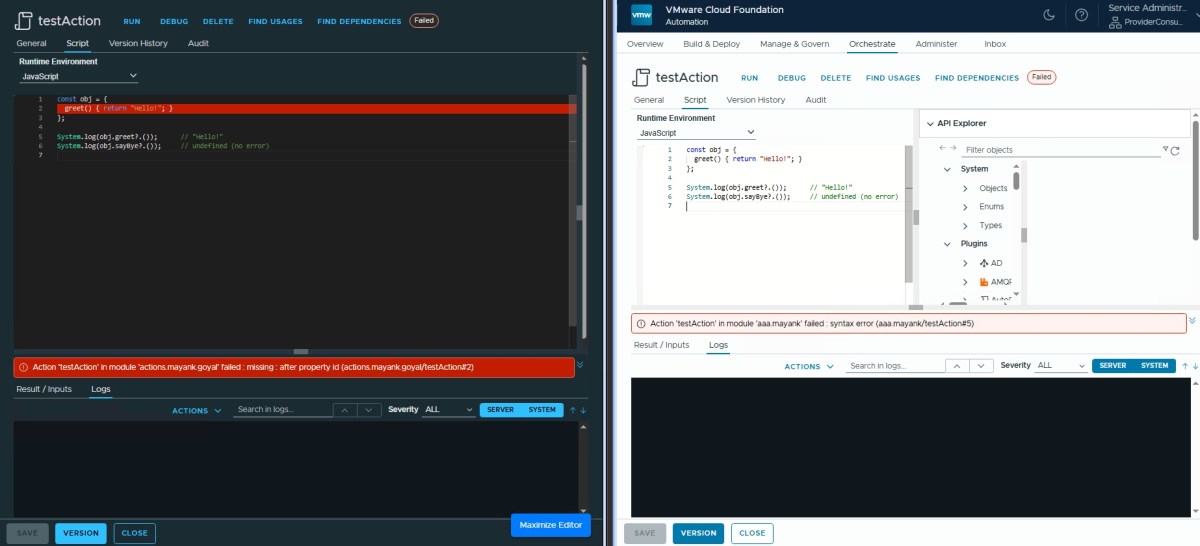
String.trimStart/trimEnd ✅
System.log(" hello ".trimStart()); // "hello "
System.log(" hello ".trimEnd()); // " hello"
Object.hasOwn ✅
// Object.hasOwn - safer alternative to hasOwnProperty
var obj = { name: "Alice", age: 30 };
System.log(Object.hasOwn(obj, "name")); // true
System.log(Object.hasOwn(obj, "toString")); // false
// Works with null prototype objects
var nullProto = Object.create(null);
nullProto.prop = "value";
System.log(Object.hasOwn(nullProto, "prop")); // true
// obj.hasOwnProperty would fail here
// Safer than hasOwnProperty
var dangerous = {
hasOwnProperty: function() { return false; }
};
System.log(dangerous.hasOwnProperty("anything")); // false (overridden)
System.log(Object.hasOwn(dangerous, "hasOwnProperty")); // true
Iterators & Array Comprehensions ✅
let arr = [1, 2, 3];
let it = arr[Symbol.iterator]();
System.log(it.next()); // { value: 1, done: false }Test code execution screenshot is included as part of other topic.
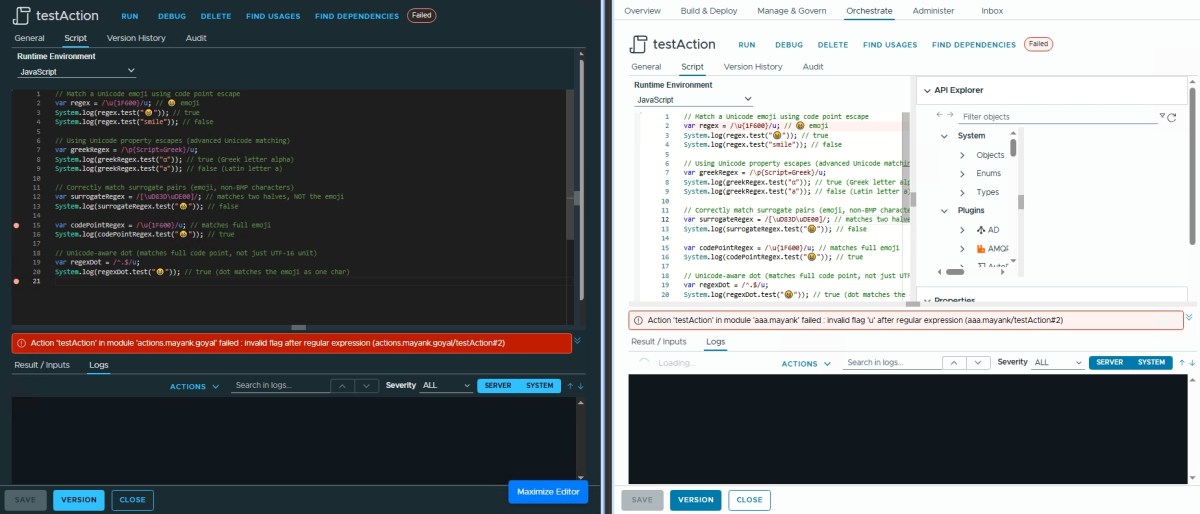
Regex Sticky Flag (y) & Unicode Flag (u) ❌
Fails with invalid flag "u" in version 9.x
// Match a Unicode emoji using code point escape
var regex = /\u{1F600}/u; // 😀 emoji
System.log(regex.test("😀")); // true
System.log(regex.test("smile")); // false
// Using Unicode property escapes (advanced Unicode matching)
var greekRegex = /\p{Script=Greek}/u;
System.log(greekRegex.test("α")); // true (Greek letter alpha)
System.log(greekRegex.test("a")); // false (Latin letter a)
// Correctly match surrogate pairs (emoji, non-BMP characters)
var surrogateRegex = /[\uD83D\uDE00]/; // matches two halves, NOT the emoji
System.log(surrogateRegex.test("😀")); // false
var codePointRegex = /\u{1F600}/u; // matches full emoji
System.log(codePointRegex.test("😀")); // true
// Unicode-aware dot (matches full code point, not just UTF-16 unit)
var regexDot = /^.$/u;
System.log(regexDot.test("😀")); // true (dot matches the emoji as one char)
JSON Superset ❔
var jsonText = '"\\u2028"';
System.log(JSON.parse(jsonText));TO BE TESTED…
String.raw ✅
var path = String.raw`C:\Users\Admin\Documents\myfile.txt`;
System.log(path); // C:\Users\Admin\Documents\myfile.txt
var message = String.raw`Line 1\nLine 2`;
System.log(message); // Outputs: Line 1\nLine 2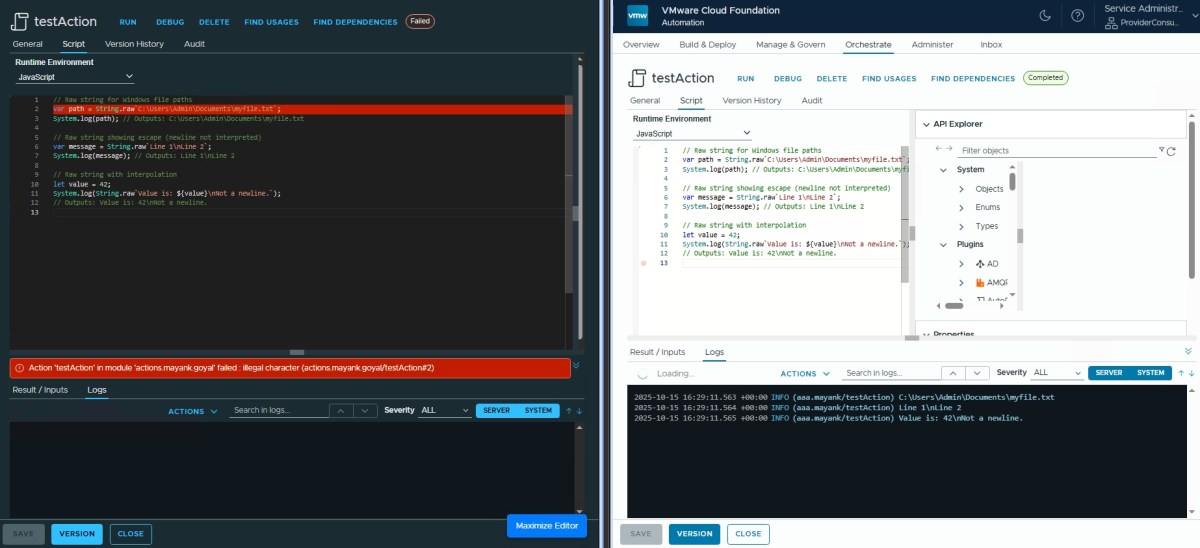
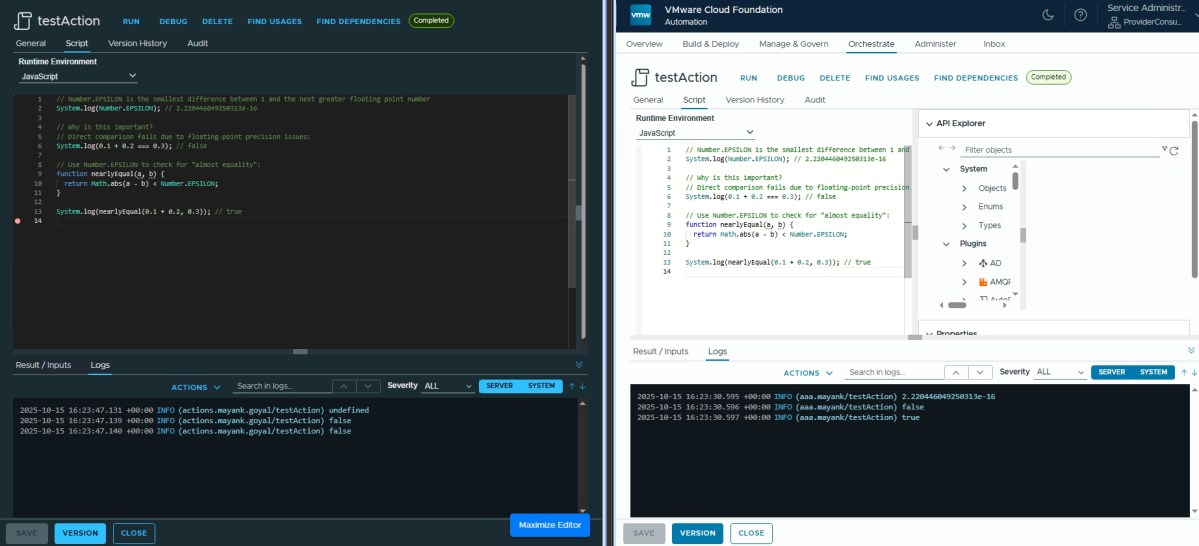
Number.EPSILON ✅
// Number.EPSILON is the smallest difference between 1 and the next greater floating point number
System.log(Number.EPSILON); // 2.220446049250313e-16
// Why is this important?
// Direct comparison fails due to floating-point precision issues:
System.log(0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3); // false
// Use Number.EPSILON to check for "almost equality":
function nearlyEqual(a, b) {
return Math.abs(a - b) < Number.EPSILON;
}
System.log(nearlyEqual(0.1 + 0.2, 0.3)); // true
Java Interoperability (Hashmap ✅ & ArrayList ❌)
// Java Map direct access (if enabled)
var HashMap = java.util.HashMap;
var map = new HashMap();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key2", "value2");
// Direct property access
System.log(map.key1); // "value1"
System.log(map["key2"]); // "value2"
// Java List with Array methods
var ArrayList = java.util.ArrayList;
var list = new ArrayList();
list.add("apple");
list.add("banana");
list.add("cherry");
// Use delete operator
delete list[1]; // Removes "banana"
System.log(list.size()); // 2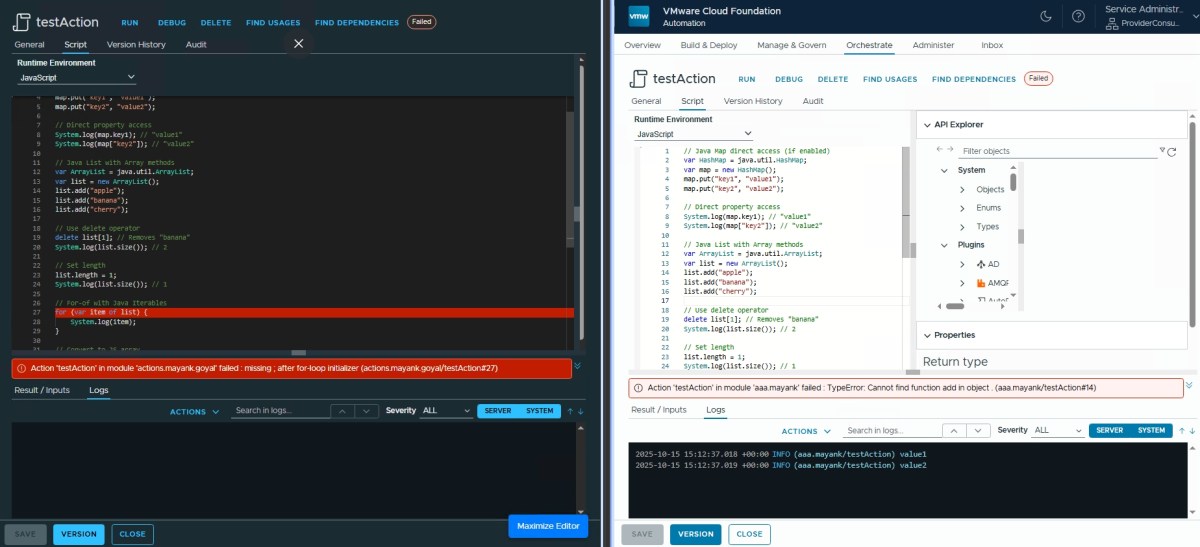
globalThis Object Reference ✅
// Universal global object reference
// Works in all environments (browser, Node.js, Rhino)
System.log(typeof globalThis); // "object"
// Set global variable
globalThis.myGlobalVar = "Hello from global";
System.log(myGlobalVar); // "Hello from global"
// Access global functions
globalThis.myFunction = function() {
return "I'm global";
};
System.log(myFunction()); // "I'm global"
Error.stack ✅
// Error stack traces
function level3() {
throw new Error("Something went wrong");
}
function level2() {
level3();
}
function level1() {
level2();
}
try {
level1();
} catch (e) {
System.log(e.message); // Something went wrong
System.log(e.stack); // Full stack trace
}
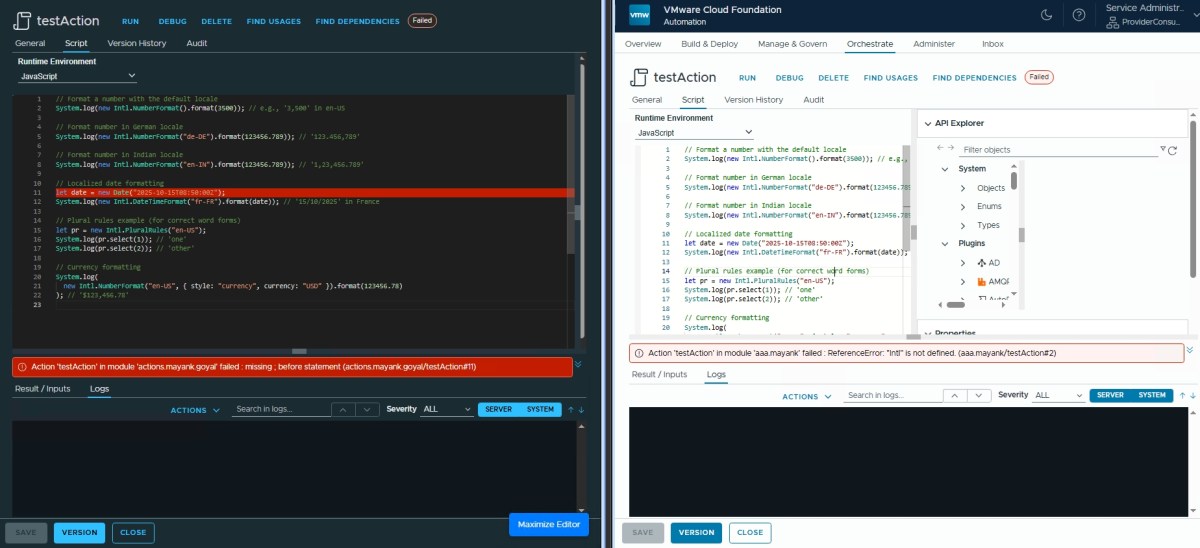
INTL (Internationalization) ❌
Fails with Reference Error “Intl”.
// Format a number with the default locale
System.log(new Intl.NumberFormat().format(3500)); // e.g., '3,500' in en-US
// Format number in German locale
System.log(new Intl.NumberFormat("de-DE").format(123456.789)); // '123.456,789'
// Format number in Indian locale
System.log(new Intl.NumberFormat("en-IN").format(123456.789)); // '1,23,456.789'
// Localized date formatting
let date = new Date("2025-10-15T08:50:00Z");
System.log(new Intl.DateTimeFormat("fr-FR").format(date)); // '15/10/2025' in France
// Plural rules example (for correct word forms)
let pr = new Intl.PluralRules("en-US");
System.log(pr.select(1)); // 'one'
System.log(pr.select(2)); // 'other'
// Currency formatting
System.log(
new Intl.NumberFormat("en-US", { style: "currency", currency: "USD" }).format(123456.78)
); // '$123,456.78'
Conclusion: Upgrade to Modern JavaScript in Orchestrator 9.x
Migrating to Orchestrator 9.x unleashes robust ES2015+ features, Unicode and locale support, and dramatically improves development speed, safety, and script modernization for all your automation needs.
Ready to modernize your workflows? Explore these features in your own vRO environment and share your migration stories below!
Discover more from Cloud Blogger
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.